Prof M Soleimani
Industrial process tomography
There
is growing interest in using real-time tomography to monitor complex industrial
processes. It is often important to know what is happening within a pipe, a
vat, or a reaction vessel, and tomography provides a convenient and
non-invasive way of doing this. We are particularly interested in novel
techniques, such as tomography based on the electrical or magnetic properties
of an object. Please contact Manuchehr
Soleimani for potential collaboration in these imaging techniques.
Electrical and magnetic tomography
For
industrial tomography, the emphasis is usually on high speed data acquisition,
rather than resolution. This lends itself to electrical tomography techniques,
which although lacking the resolution of X-ray
and MRI tomography, are nearly instantaneous. Examples of electrical
tomographic imaging methods are:
Electrical
Impedance Tomography (EIT), in which measurements of resistance between different combinations of electrodes,
are used to determine the internal resistivity of an object.
Electrical
Capacitance Tomography (ECT), in which multiple measurements of capacitance between different combinations of metal plates
placed around the object, are used to determine the internal dielectric
permittivity of an object.
Magnetic
Permeability Tomography (MPT), in which multiple measurements of
coupling between different combinations of magnets and magnetometers are used
to determine the internal magnetic properties of an object.
Magnetic
Induction Tomography (MIT), in which multiple measurements of
coupling between magnetic excitation and sensing coils are used to determine
the internal resistivity of an object.
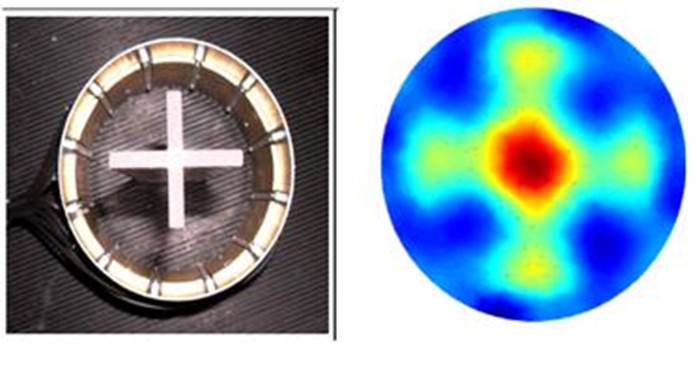
Object
(left) imaged (right) with electrical capacitance tomography.
Ultrasound Tomography
In
Ultrasound Tomography (UST), pulses of very high frequency sound (typically in
the order of megahertz) are fired into the object to be observed. Ultrasound
detectors are used to measure the time-of-flight to different locations on the
objects surface. This time-of-flight depends on the physical properties of the
intervening material, and so contains information about the object's interior.
Multiple measurements can be used to reconstruct the object's internal
composition. We are developing a UST device to measure the internal composition
of a fluid-filled vessel. It can measure velocity throughout the fluid, and
detect the presence of solid objects, or gas bubbles.
Tomography Hardware
We
are currently constructing a range of imaging devices, many of which are based
on these principles. See the Engineering
tomography lab web page for more information.
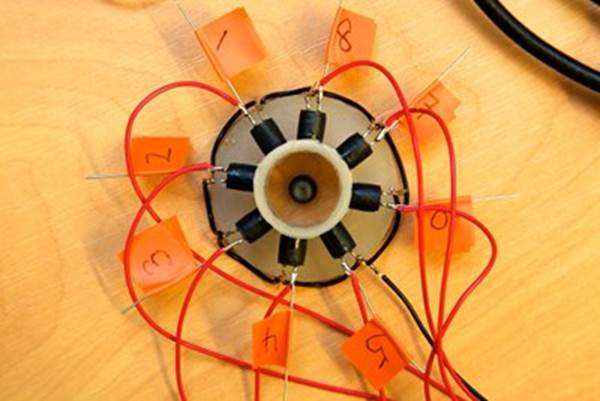
Prototype
magnetic induction tomography device.
Tomography software
We
have developed the tomography software for ECT, MIT, EIT, Ultrasound tomography
and cone-beam CT all in 2D and 3D. As an example electrical tomography is a
difficult mathematical problem, as the inverse problem is nonlinear. Therefore, much of the research in this field is
still concerned with developing usable algorithms. Noise is a major problem, as
it can be interpreted as the presence of physical features which aren't
actually there. In the example below, EIT measurements of test objects (shown
left) were simulated, and noise was added to the data. Using conventional
algorithms (shown centre), this noise gives the strong impression of other
features. With a newer algorithm, these artefacts are greatly reduced.
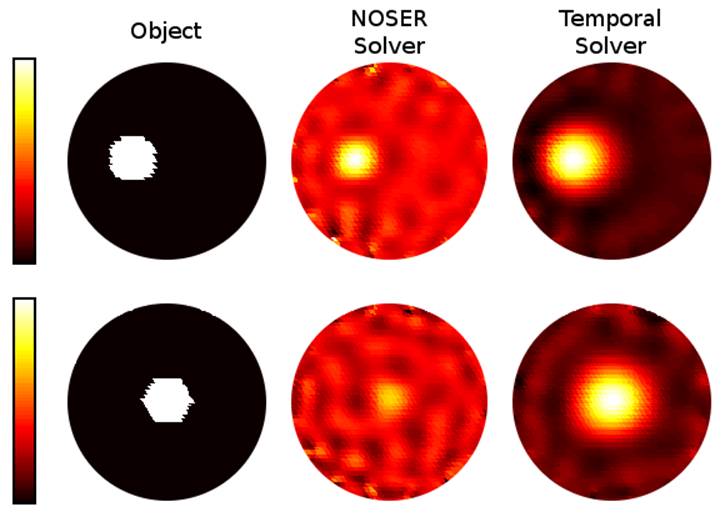

Comparison of algorithms for electrical impedance tomography.