Ph.D Research
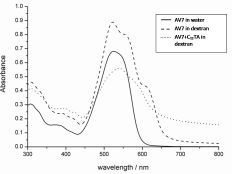
Optically and physically anisotropic particles were synthesised from dyes and surfactants using ionic self-assembly. This means the ionic building blocks organise themselves into more complex structures. The optical properties of the particles were studied by Polarised Optical Microscopy (POM), and Dichroic Ratios (DR) were measured by UV-Visible spectroscopy. The stability of the particles in a variety of organic solvents was also quantified.
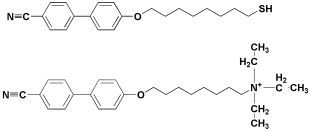
In addition, mesogenic stabilisers similar in chemical structure to the liquid crystal 4-n-pentyl-4(')-cyanobiphenyl (5CB) were synthesised with both trimethylammonium (–N(CH3)3) and thiol
(–SH) functionalisation. The trimethylammonium functionalised mesogenic stabiliser was then used to attempt suspension of montmorillonite clay within a 5CB sample. The thiolated mesogenic stabiliser was used to suspend silver nanoparticles within a 5CB sample.
The physical properties of the dichroic particles and stabilisers were quantified by means of various analytical techniques such as: